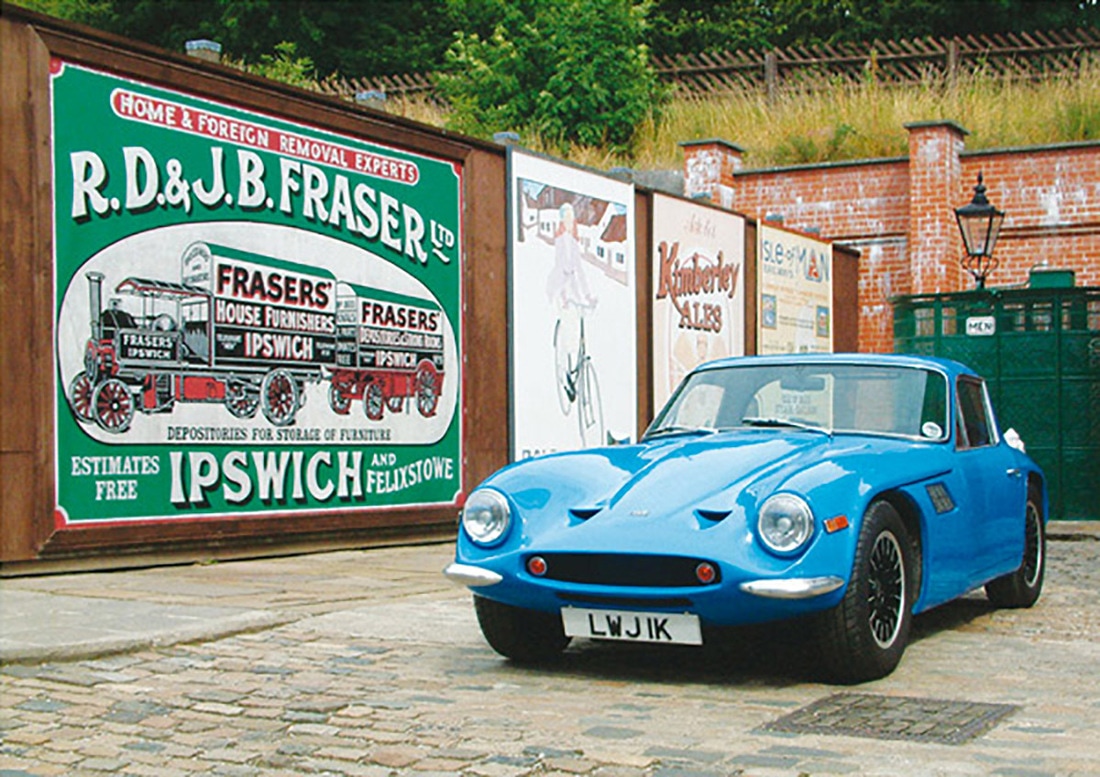
History1965 - Following the purchase of TVR by Martin and Arthur Lilley in 1965, they set about updating the model range. They took the existing Grantura Mk III chassis and used this to create the Grantura MkIV/1800S which in turn, with an engine transplant replacing the MGB engine with a Ford Cortina GT 1600 crossflow, became the first of the new Vixens in 1967. In fact, so much was the Vixen a continuation of the 1800S that sveral of the 117 Vixen S1s built had MGB engines. In October of the following year, the Vixen S1 gave way to the S2 variant which although mechanically very similar, took the 4.5 inch longer chassis from the LWB Tuscan which meant that longer doors could be fitted to improve access to/from the cabin.
1968 - The S2 had over 75 improvements when compared to the S1 and it quickly proved to be a popular model, selling 438 in just two years and making it the then most popular TVR to date. From a modern restorer’s perspective, the most important change is that this was the first TVR in which the body was bolted to the multi-tubular chassis rather than being bonded which had happened previously. It also had longer doors, a restyled bonnet and new square tail lights from the Ford Cortina Mk2 replaced the Cortina Mk1 'ban the bomb' ones. The Vixen S2 was the first car to deliver a profit for TVR in any of its incarnations. The Grantura MkIII, MkIV 1800s and Griffith all had a short wheelbase, as did the Vixen S1. The body of these cars was bonded onto their multi-tubular chassis. The Vixen S2 had a longer wheelbase and the body was bolted on to the chassis which was the case all subsequent TVRs. The Vixen S3 was launched in October 1970, and now used the Ford 4 cylinder engine producing 92bhp as fitted to the Ford Capri. It looks almost identical to the S2, save for the 'Aeroflow' grilles for the wing vents, taken from the C-pillar of the Ford Zodiac Mk4. 1971 - The 1300 was produced as a cheaper model, using the 1296cc Triumph Spitfire engine. With only 63bhp and performance was poor and demand was low, at just 15 cars. At the same time the 2500 was produced using a Triumph 2.5 straight six engine which had certification for US emissions. 1972 - The S4 was produced as an interim model using the new TVR M series chassis with a Vixen body, just 23 cars were built. The body sat higher than on the older round tube chassis and the square tubes are visible in the front wheel arches. Of the 385 2500S built 96 had the M Series chassis, with virtually all being exported to the USA. The final six 1300s were produced on the M chassis. |
Technical SpecificationsTVR Vixen S1
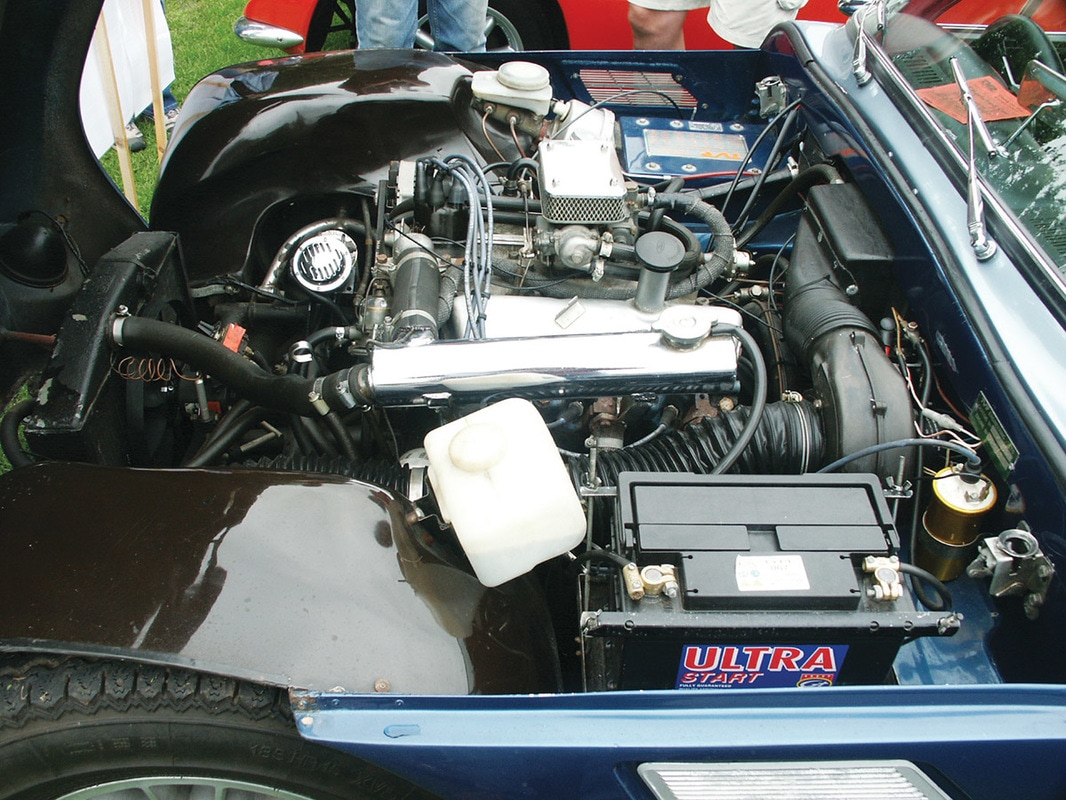
Engine: Ford Cortina GT Crossflow Capacity (cc): 1599cc Power: 88bhp @ 5400rpm Torque: 96lbft @ 3600rpm Performance: 0-60mph 10.5secs Suspension & Brakes: All round independent suspension with wishbones and coil springs / telescopic dampers. Wheels and Tyres: 4.5x15 inch wire wheels with 165-15in tyres TVR Vixen 1300
Engine: Triumph Spitfire 1300 Capacity (cc): 1296cc Power: 63bhp Top speed: 90mph Production Numbers:
Vixen S1 - 117 Vixen S2 - 438 Vixen S3 - 165 Vixen S4 - 23 1300 - 15 2500 - 385 |
|
ARCHIVES
Find out more in the Pre-M Series Archives (Members Only) |
TECHNICAL
Find out more on the Pre-M Series Technical Page (Members Only) |
Details or adverts from the period
Photos, additions or changes to this page - did we get anything wrong or do you have anything we could add?
We would love to hear from you
We would love to hear from you